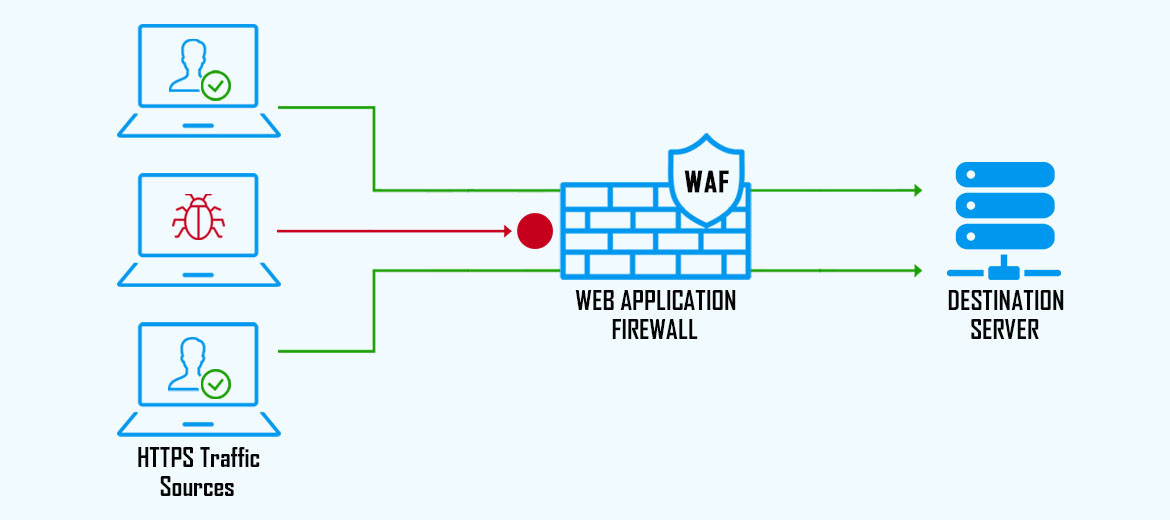
A WAF or web application firewall is a virtual security appliance or cloud service designed to protect organizations at the application level by filtering, monitoring, and analyzing traffic over Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure ( HTTPS) between web applications and the Internet.
How does a WAF work?
A WAF can be software, a device, or a service. It analyzes HTTP requests and applies a set of rules that define which parts of the conversation are benign and which parts are malicious.
The main parts of HTTP conversations that a WAF analyzes are GET and POST requests. GET requests are used to retrieve data from the server and POST requests are used to send data to a server to change its state.
WAFs work through policies that determine what malicious traffic and safe traffic look like. Broadly, these policies fall into two categories: a blocking model, where traffic that resembles known attacks is not allowed to pass through the WAF, and an authorization model, where traffic that is pre-approved will be allowed to pass. Most WAFs do not rely exclusively on single model policies, as each model has inherent weaknesses. Therefore, WAFs tend to use a hybrid model with both blocking and permitting policies for maximum efficiency.
A WAF can take one of the following three approaches to parse and filter the content in these HTTP requests:
- White list
The WAF by default denies all requests and only allows requests that are known to be trusted. It provides a list of IP addresses that are known to be safe. Whitelisting is less resource intensive than blacklisting. The downside of whitelisting is that it can inadvertently block benign traffic. While it casts a wide net and can be effective, it can also be imprecise.
- Blacklist
The blacklist uses predefined signatures to block malicious web traffic and protect the vulnerabilities of websites or web applications. It is a list of rules that indicate malicious packets. Blacklisting is suitable for public websites and applications because they receive a lot of traffic from unknown IP addresses, which are not known to be malicious or benign. The disadvantage of blacklisting is that it requires more resources and more information to filter packets based on specific characteristics, as opposed to the default filtering of trusted IP addresses.
- Hybrid security
A hybrid security model uses both blacklist and whitelist elements at the same time.
Ways to deploy a WAF
There are three main ways to deploy a WAF on a web server: network-based, host-based, or cloud-based.
- Network-based WAF
In a network-based WAF, hardware or physical equipment interpose s between server and client traffic. The main advantage of network-based WAFs is that they minimize latency because protection works through a separate physical device on-site. However, network-based WAFs are usually the most expensive option.
- Host-based WAF
In the case of host-based WAF, protection comes from software installed on the web server itself. Like network-based WAFs, host-based WAFs are on-site and therefore minimize latency. However, host-based WAFs consume web server resources to perform their protection function because they do not reside on a separate physical device, unlike network-based WAFs. Thus, host-based WAFs can also be expensive due to the need to optimize a web server so that its performance is not degraded by implementing a host-based WAF on the server itself.
- Cloud-based WAF
The main advantages of cloud-based WAFs are affordability and simplicity. Cloud-based WAFs are typically offered as a service for a monthly fee and do not require large upfront investments, such as purchasing physical equipment, like network-based WAFs. Cloud-based WAFs are also very easy to deploy. Often, a DNS change is enough to redirect traffic to the cloud-based WAF service. The main disadvantage of cloud-based WAFs is that the protection is not on-site and the end user is not fully aware of the policies and strategies used because the protection is provided by a third party.
To launch a new solution, you can purchase your favorite domains at the most convenient prices using a quick domain registration solution and invest in a secure and optimal hosting plan - choosing an NSHOST hosting solution web shared, VPS or Cloud. It recommends paying close attention to the strategy of caching suitable for your business to ensure optimal loading times for each web page.